Did You Know?
Terima kasih Pengunjungku :

Custom Search
Thursday, January 7, 2010
Synthesising the concept of transport of substances in plants.
Learning Outcomes :
A student is able to :
* state what translocation is,
* explain the importance of translocation in plants,
* describe the process of transpiration,
* explain the importance of transpiration,
* state external conditions affecting transpiration.
Learning Outcomes :
A student is able to :
* state what translocation is,
* explain the importance of translocation in plants,
* describe the process of transpiration,
* explain the importance of transpiration,
* state external conditions affecting transpiration.
1. Translocation
- The two-directional transport of dissolved organic solutes in the phloem is known as translocation.
- Translocation is important to plants because organic substances such as sugars and amino acids are transported from the leaves to the storage organs , to the growing regions for growth and development and to the cells for metabolism. This is important for the survival of the plant.
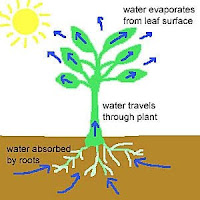
2. Transpiration
 Transpiration is the loss of water vapour through the evaporation in plants (alomost 90% of water contained in a plant).
Transpiration is the loss of water vapour through the evaporation in plants (alomost 90% of water contained in a plant).- Water is lost through the stomata of leaves.
- Stomata control the rate at which transpiration occurs. The opening of the stomata is controlled by guard cells that gain and loss water, which close and open the stomata respectively.
- When the water pressure in the guard cells becomes greater than in the surrounding cells, the stomata open allowing transpiration.
- Transpiration is important to the plant because :
it helps in the absorption and transport of water and mineral ions from the roots to different parts of the plant.
it helps to cool the plant.
it helps to supply water to all plant cells for metabolic processes.
it helps to prevent plants from wilting by helping them to maintain cell turgidity
3. The process of transpiration
- Water is lost from the external surfaces of the mesophyll cells of the leaves by evaporation.
- The air spaces in the mesophyll are saturated with water vapour.
- The air in the atmosphere outside the stomata is less saturated with water.
- As a result, water vapour in the air spaces of the leaf diffuses from the plant cells into the atmosphere through the stomata.
- The movement of air outside the leaf carries water vapour away from the stomata.
- The loss of water from a mesophyll cell makes the cell hypertonic to an adjacent cell.
- Water from the adjacent cell diffuses into the mesophyll cell by osmosis and this in turn draws water from another adjacent cell into this cell.
- Water continues to diffuse from neighbouring cells into the adjacent cells.
- Finally, water is drawn from the xylem vessels in the veins.
- A pulling force is created to pull water up the xylem vessels as a result of the evaporation of water vapour and this is known as transpirational pull.
In the presence of light, glucose synthesised will increase the osmotic pressure of the guard cell. The guard cells will absorb water through osmosis and become turgid. High hydrostatic pressure causes stomata to open. The rate of transpiration increases.
In the dark, photosynthesis do not occur and the concentration of glucose in the guard cell decreases. The osmotic pressure in the cell also decreases. Water moves out from the cells by osmosis. The guard cells become flaccid and the stomata close. The rate of transpiration decreases.
4. Factors affecting the rate of transpiration
- Light intensity : An increase in light intensity increases the rate of transpiration. Thus, transpiration is high during the day and radically drop at night.
- Temperature : An increase in temperature increases the rate of transpiration.
- Air movement : An increase in air movement increases the rate of transpiration. Thus, transpiration is higher on a windy day.
- Relative humidity : High humidity surrounding the leaves reduces the rate of transpiration. The higher the humidity of the surrounding atmosphere, the lower is the rate of transpiration.
Source :
http://ckgbio.blogspot.com/search/label/Chapter%201%20Form%205
0 Comments:
Subscribe to:
Post Comments (Atom)